TiWorker.exe is the Windows Update Trusted Installer Worker process, a sub-process of the TrustedInstaller system utility. It’s also called the Windows Modules Installer Worker (WMI Worker), and it’s vital in updating your computer’s operating system. TiWorker.exe runs in the background, checking for available updates or downloading system updates.
The process may have high CPU usage when performing its responsibilities. But it’s unusual for TiWorker.exe to stay active in the background or consume system resources excessively. This tutorial highlights different ways to fix TiWorker.exe high disk usage in Windows 10 and 11.

Manually Install Windows Updates or Restart Your PC
Tiworker.exe may use system resources if there are missing or pending Windows Updates. Manually installing updates can fix the issue.
- Go to Settings > Windows Update and select Check for updates.
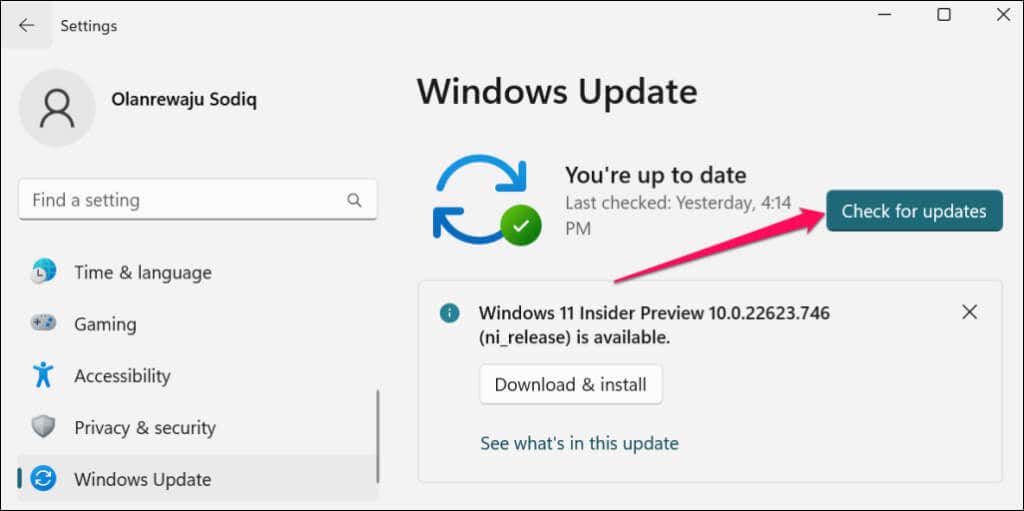
- Select Restart now if there’s a pending Windows Update installation.
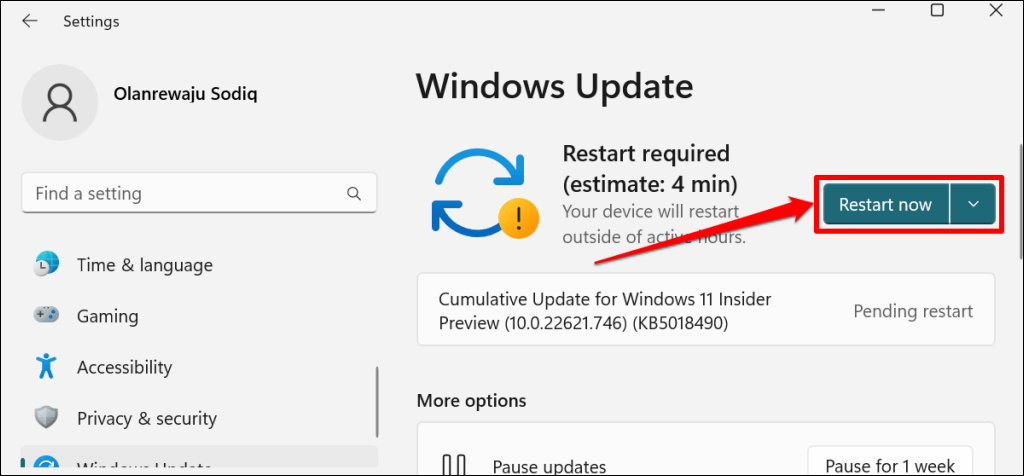
- In Windows 10, head to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and select Check for updates or Restart now.
Rebooting your computer can also reduce TiWorker.exe’s CPU usage. Close your apps before restarting your PC, so you don’t lose unsaved data.
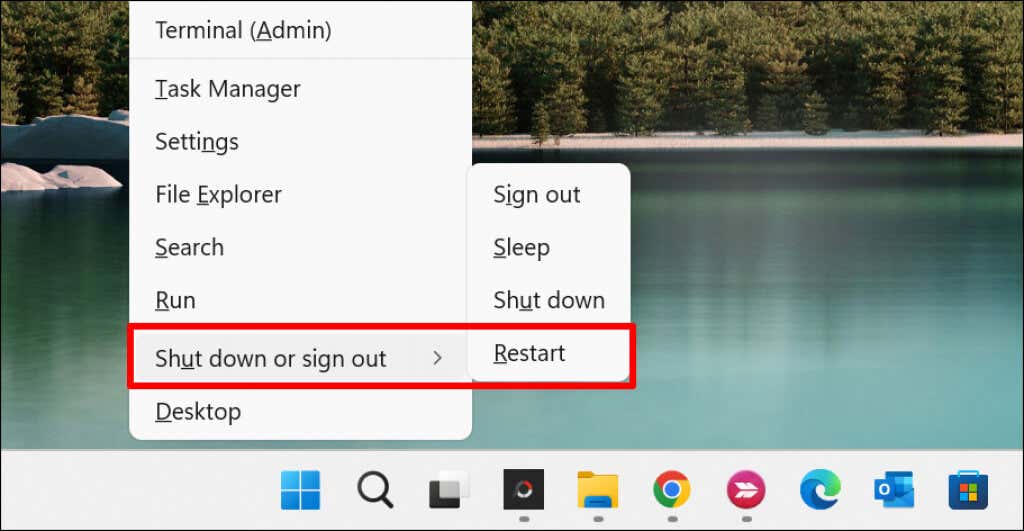
- Press the Windows key + X, select the Power icon in the Start menu, and select Restart.
Open Task Manager and check TiWorker.exe’s CPU usage. Try the next troubleshooting solution if TiWorker.exe continues to use excessive system resources.
Run the Windows Update Troubleshooter
The Windows Update troubleshooting tool can diagnose and fix issues spiking TiWorker’s CPU usage.
- Go to Settings > System > Troubleshoot and select Other troubleshooters.
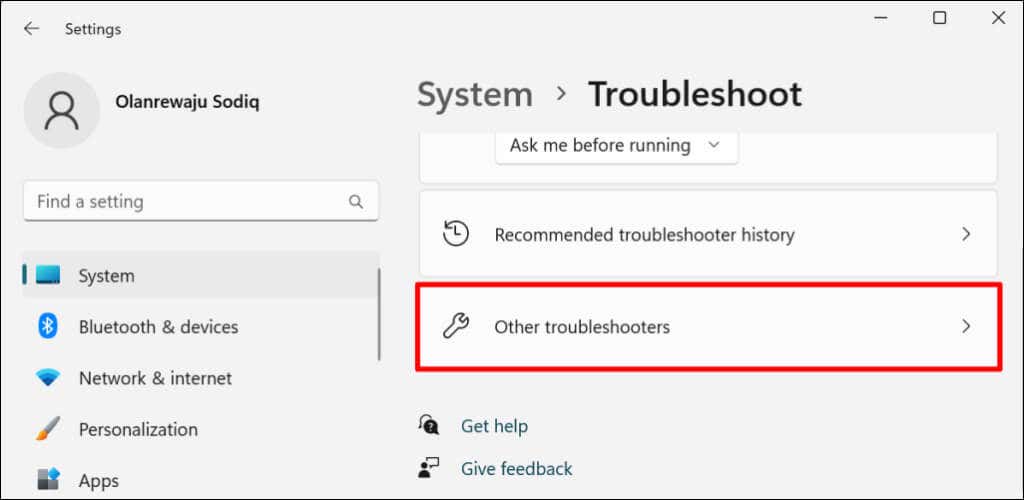
- Select Run next to “Windows Update.”
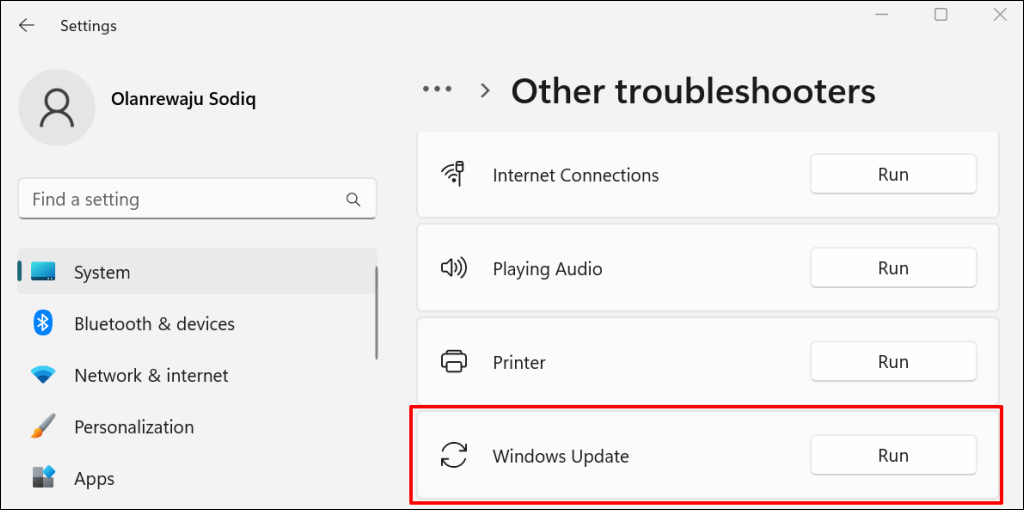
The troubleshooter will scan your computer for Windows Update issues and fix them.
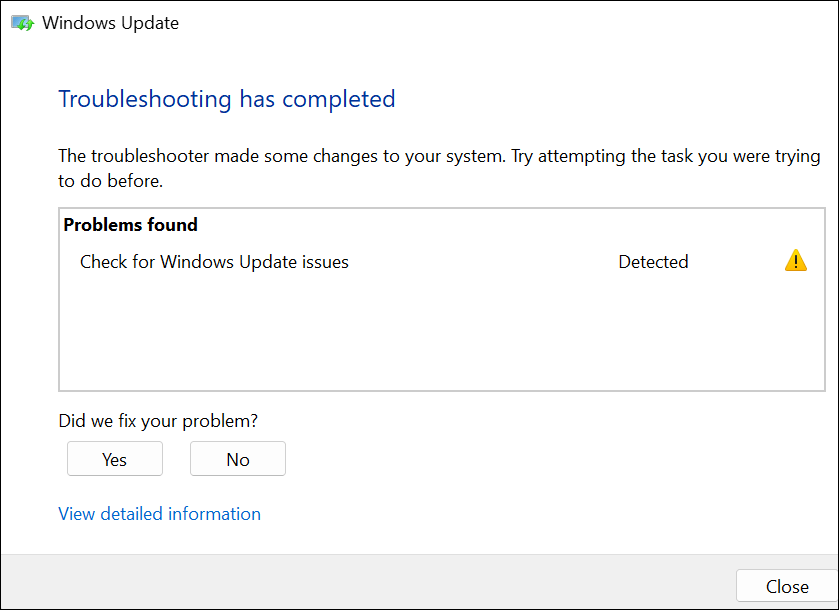
Close the troubleshooter and check TiWorker.exe CPU usage in the Task Manager. Run the System Maintenance troubleshooter if the problem persists.
Run the System Maintenance Troubleshooter
The Windows System Maintenance tool can also tone down TiWorker.exe’s CPU usage.
- Open the Control Panel, set the “View by” option to Large icons, and select Troubleshooting.
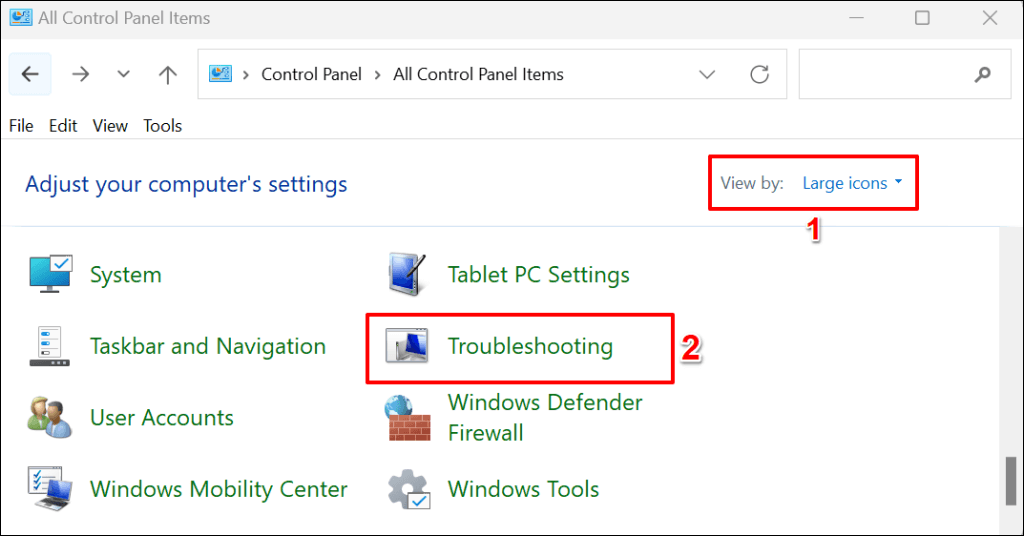
- Select View all on the sidebar.
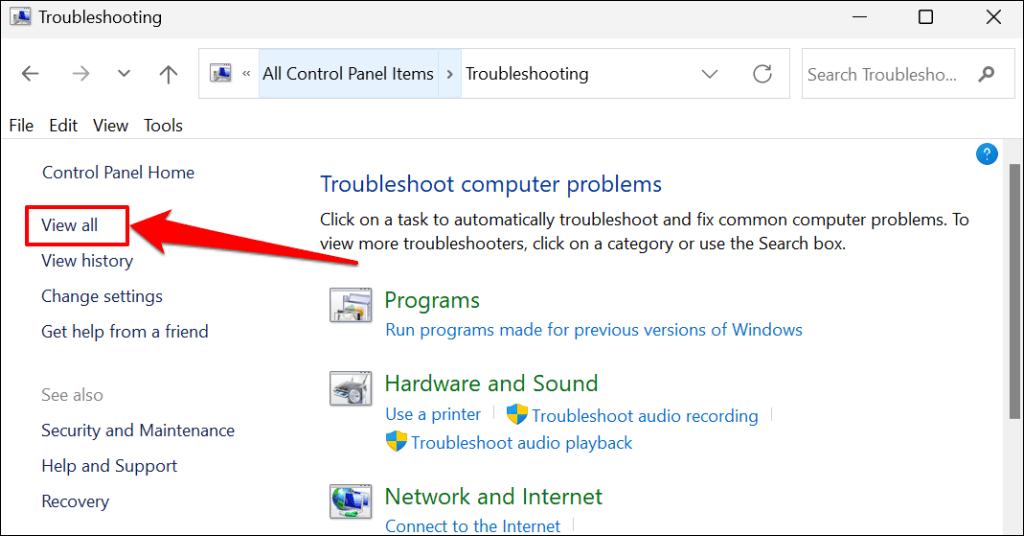
- Select System Maintenance.
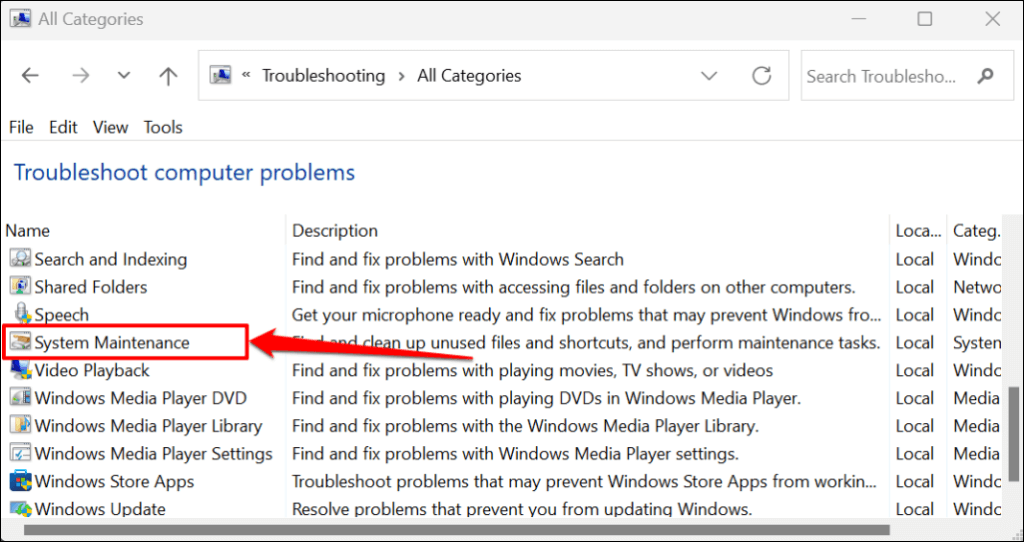
Quick Tip: You can also run the System Maintenance troubleshooter through the Windows Run box. Press Windows key + R, paste %systemroot%system32msdt.exe -id MaintenanceDiagnostic in the dialog box, and press OK.
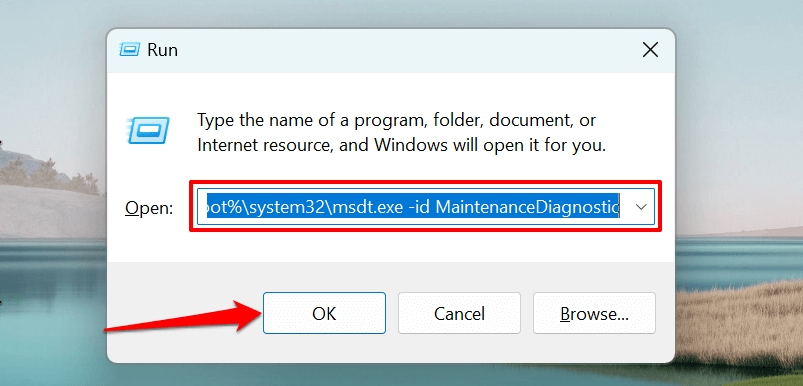
- Select Advanced.
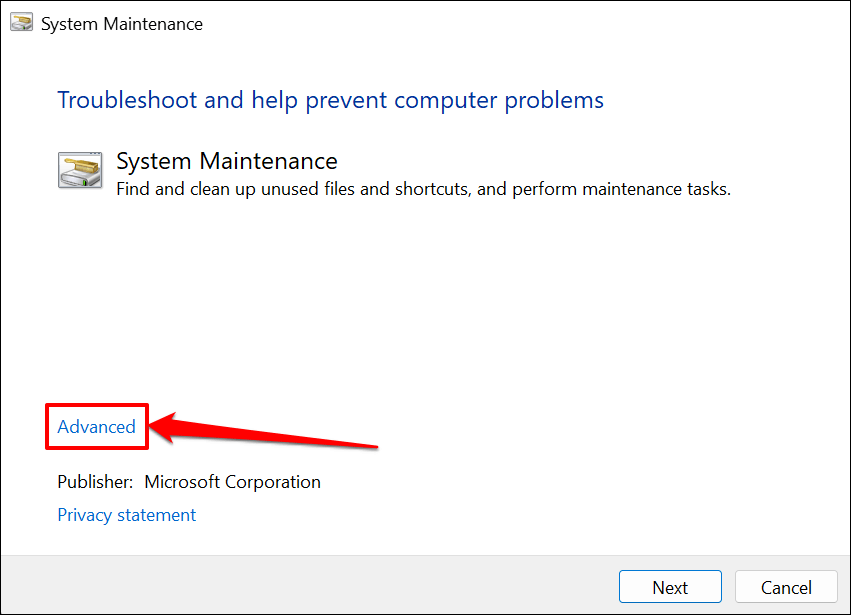
- Check Apply repairs automatically and select Run as administrator.
- Select Next to proceed.
Close the System Maintenance tool when it completes the troubleshooting checks. Restart your computer if the TiWorker.exe high CPU usage issue persists.
Run the System File Checker
System File Checker (SFC) is a command-line tool that repairs and replaces corrupted system files. SFC can fix Windows Updates files causing TiWorker.exe to use high CPU resources.
Connect your computer to the internet and follow the steps below to run an SFC scan.
- Press the Windows key, type cmd in the search bar, and select Run as administrator below the Command Prompt app.
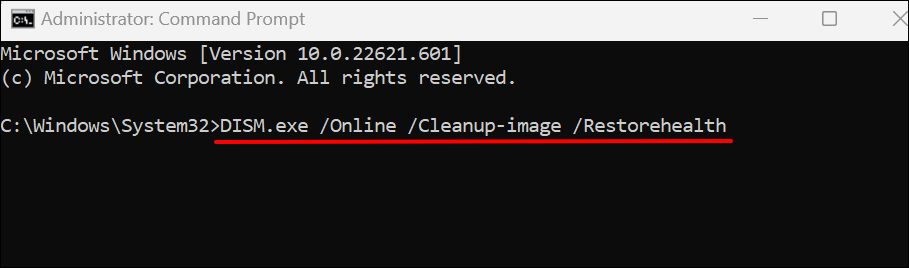
- Paste DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth in the console and press Enter.
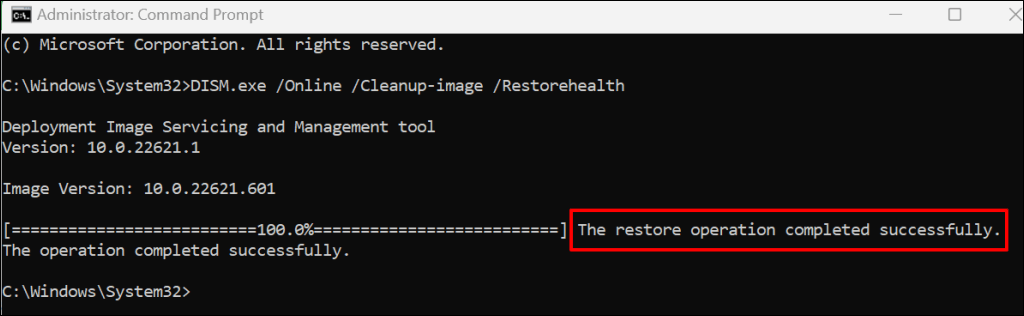
The command prompts the Windows Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool to download files required to fix or replace corrupt files. The DISM command-line tool can also fix a host of Windows Update errors. Run the next command when Command Prompt displays a “The restore operation completed successfully.” message.
- Paste sfc /scannow in the console and press Enter.
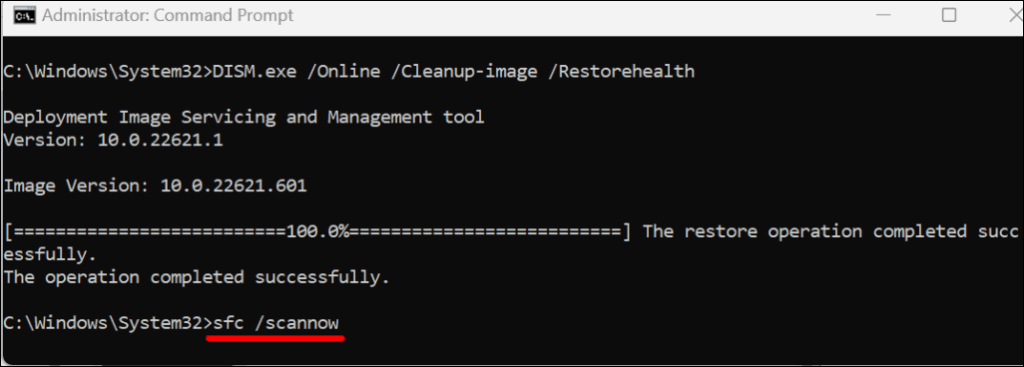
The System File Checker will scan your computer and replace any corrupt system file it finds. The file verification and repair process may take up to 30 minutes.
If SFC repairs any file, Command Prompt displays a “Windows Resource Protection found corrupt files and successfully repaired them” message.
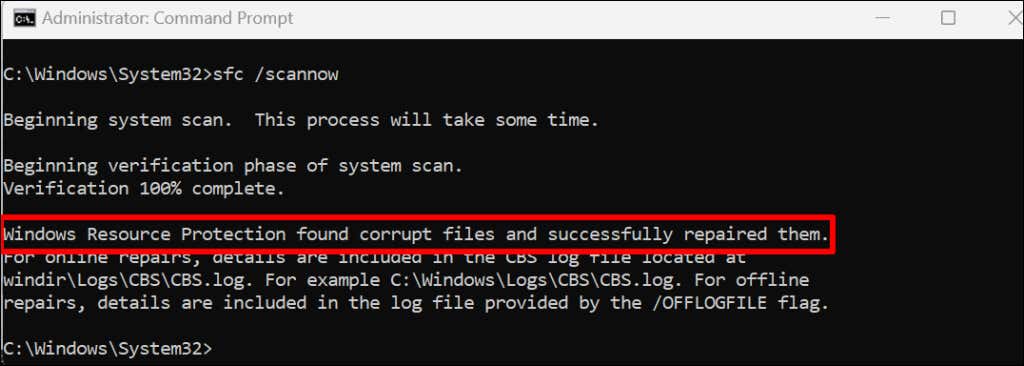
Close Command Prompt, reboot your computer, and check if the file repair process gets TiWorker.exe working correctly.
Perform a Clean Boot
A clean boot can help you detect apps or programs preventing your computer from installing a Windows Update. Clean booting your PC disables non-essential Microsoft services and starts a minimum number of programs and drivers. It’s similar to booting Windows in Safe Mode.
Perform a clean boot, enable one service at a time, reboot your computer, and check TiWorker.exe CPU usage. Repeat the process until you find the app or service spiking TiWorker.exe’s CPU usage. For more information, refer to our tutorial on performing a clean boot in Windows.
Delete Windows Update Cache Files
Clearing Windows Update cache files can fix Windows Update installation issues and reduce TiWorker.exe high CPU usage.
- Open the Windows Start menu and type services.msc or services in the search bar. Select Run as administrator below the Services app.
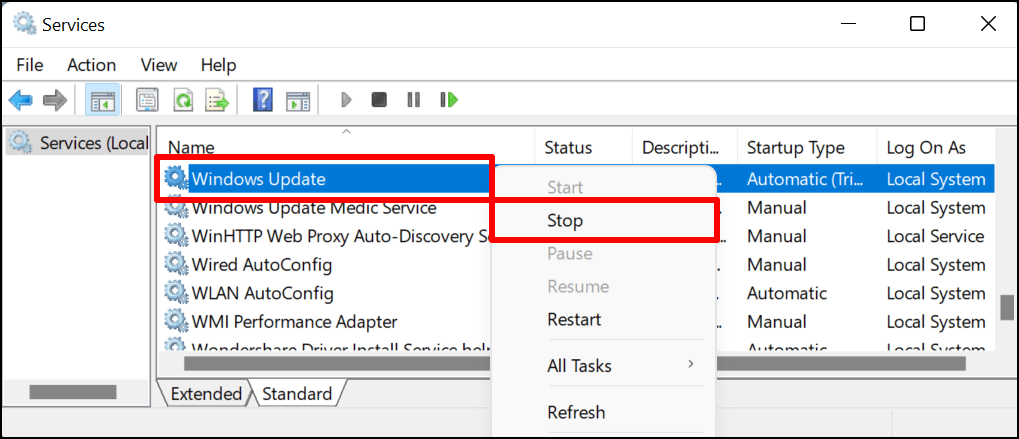
- Right-click Windows Update and select Stop on the context menu.
- Open the File Explorer, paste C:WINDOWSSoftwareDistributionDownload in the address, and press Enter.
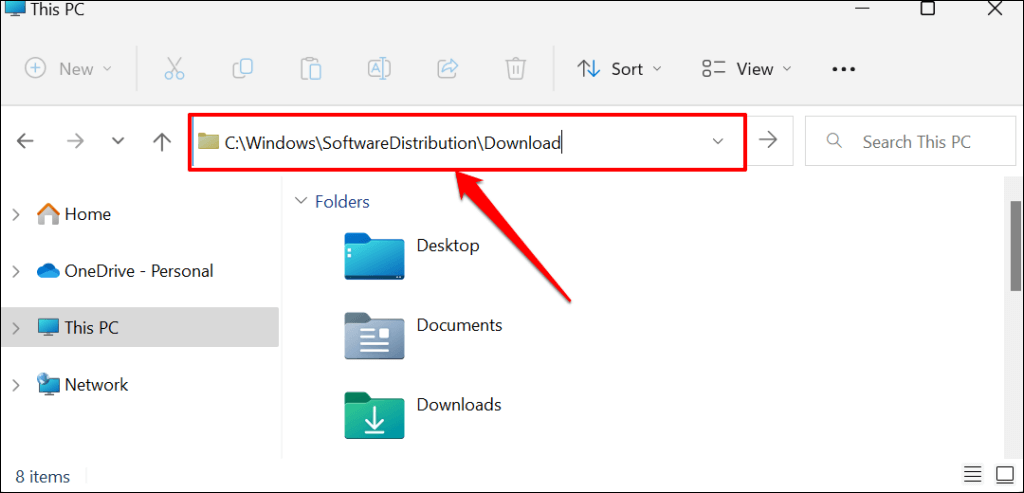
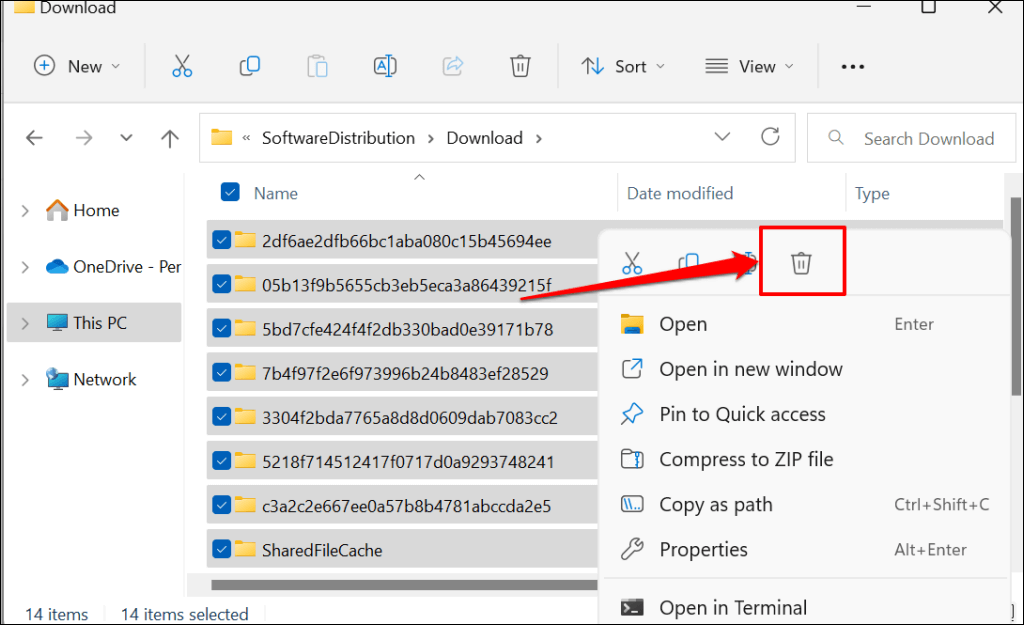
- Press Ctrl + A to select all the files in the SoftwareDistribution folder. Right-click the selection and select the Delete icon. You can back up the files to an external storage device or a different folder on your computer.
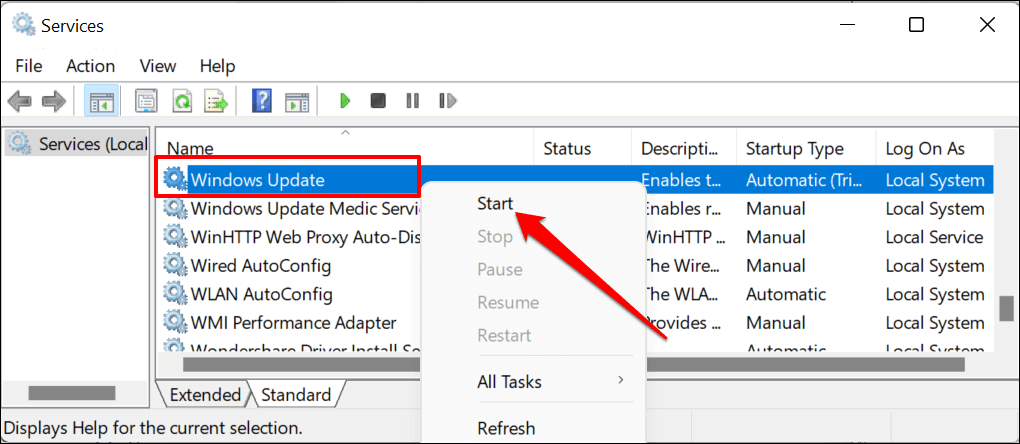
- The next step is to restart the Windows Update service. Reopen the Windows Services menu, right-click Windows Update, and select Start.
Reboot your computer and check if deleting Windows Update cache files fix TiWorker.exe high CPU usage problem.
Uninstall Conflicting HP Programs
If you have the HP Support Assistant on your computer, uninstalling the software might reduce TiWorker.exe disk usage. Some users fixed TiWorker.exe high CPU usage by uninstalling the HP LAN Assistant software.
These HP apps appear to conflict with TiWorker.exe and cause the process to use too much CPU. Delete these apps, restart your PC, and monitorTiWorker.exe’s CPU usage in the Task Manager.
TiWorker.exe Isn’t Malware
TiWorker.exe is a genuine background process that runs when checking for new updates or installing downloaded updates. The troubleshooting solutions above should fix the TiWorker.exe high CPU usage issue. Scan your computer using Windows Defender or third-party antivirus if the problem persists.
Source by helpdeskgeek.com





























